The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the child’s pillow, but they be assured of a replacement tooth in a few months. Unfortunately, the scenario is quite different for adults grappling with a loss of teeth. Luckily, there may be some hope thanks to a new study performed by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui.
A dental breakthrough
While the typical adult mouth houses 32 teeth, approximately 1% of the population exhibits variations of them, either possessing more or fewer teeth due to congenital conditions. Researchers have delved into the genetic factors behind cases of excessive teeth, seeking valuable insights into the potential regeneration of teeth in adults. This study is the first to show that monoclonal antibodies can help regrow teeth. It suggests a new way to treat a dental problem that currently requires implants and other artificial solutions.
A bit of science
The research team disclosed that an antibody targeting a specific gene, known as uterine sensitization-associated gene-1 (USAG-1), can induce tooth development in mice affected by tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The findings were published in the journal, Science Advances.
As per Katsu Takahashi, a senior lecturer at the Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine and one of the principal contributors to the study, the essential molecules crucial for the development of teeth have already been pinpointed. “The morphogenesis of individual teeth depends on the interactions of several molecules including BMP, or bone morphogenetic protein, and Wnt signaling,” says Takahashi.
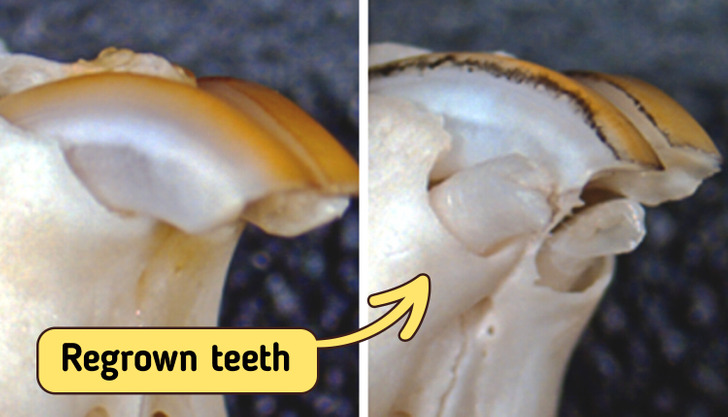
On April 13, 2021, the University of Kyoto posted its first pic of newly-grown teeth in mice.
BMP and Wnt are involved in more than just tooth development; they affect the growth of organs and tissues early in the body’s development. Because drugs affecting them directly might have broad side effects, scientists are cautious. To find a potentially safer method, researchers focused on the gene USAG-1, thinking that aiming at factors countering BMP and Wnt specifically in tooth development could be more precise.
“We knew that suppressing USAG-1 benefits tooth growth. What we did not know was whether it would be enough,” added Takahashi.
The first results
Scientists looked at how different monoclonal antibodies affect USAG-1. Monoclonal antibodies are often used to treat things like cancer and arthritis and for making vaccines. Tests with this antibody showed that BMP signaling is crucial for deciding the number of teeth in mice. Also, just one treatment was enough to grow a whole tooth. Further tests confirmed these positive results in ferrets too.
“Ferrets are diphyodont animals with similar dental patterns to humans. Our next plan is to test the antibodies on other animals, such as pigs and dogs,” explained Takahashi.
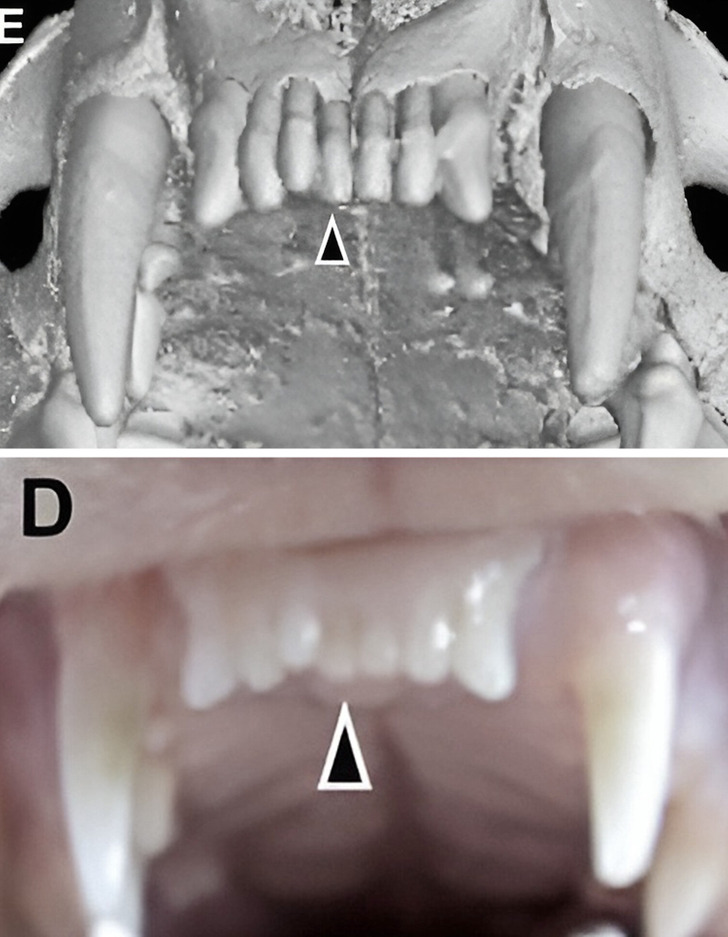
Fully regrown frontal teeth in ferrets
The next steps

Now, scientists are going to test the drug on healthy adults. If that goes well, the team plans to try it on kids aged 2 to 6 with a rare tooth problem called anodontia, a genetic disorder defined as the absence of all teeth. These kids will get one shot of the drug to see if it makes their teeth grow. If everything works out, the medicine might be approved by 2030.
Takahashi sees the new medicine as an additional choice for individuals who are missing some or all of their teeth.
“The idea of growing new teeth is every dentist’s dream,” Takahashi told the Japanese newspaper, The Mainichi in June this year. “I’ve been working on this since I was a graduate student. I was confident I’d be able to make it happen.”
So hopefully, by the year 2030, humans will get a chance to have their third generation of teeth grown and say goodbye to implants. Until then, make sure to keep your teeth strong and healthy — this article will help you with that.
Preview photo credit KyotoU_News / Twitter
I Married a Widower with a Young Son – One Day, the Boy Told Me His Real Mom Still Lives in Our House

“My real mom still lives here,” my stepson whispered one night. I laughed it off, until I started noticing strange things around our home.
When I married Ben, I thought I understood what it meant to step into the life of a widower. He had been so devoted to his late wife, Irene, and he was raising their seven-year-old son, Lucas, all on his own.

A happy father-son duo | Source: Midjourney
I respected the deep love he still held for her, knowing it was tied to the memory of his first love and Lucas’ mother. I wasn’t here to replace her, just to create a new chapter for all of us.
The first few months as a family were everything I had hoped for. Lucas welcomed me warmly, with none of the hesitation I had feared. I spent hours playing games with him, reading his favorite bedtime stories, and helping him with schoolwork.

A woman helping a young boy with homework | Source: Midjourney
I even learned to make his favorite mac and cheese exactly how he liked it — extra cheesy with breadcrumbs on top.
One day, out of nowhere, Lucas started calling me “Mom,” and every time, Ben and I would catch each other’s eye with proud smiles. It felt like things were falling perfectly into place.
One night, after a cozy evening, I was tucking Lucas into bed. Suddenly, he looked up at me, his eyes wide and serious. “You know, my real mom still lives here,” he whispered.

A young boy lying in bed at night | Source: Midjourney
I chuckled softly, running my fingers through his hair. “Oh, sweetheart, your mom will always be with you, in your heart.”
But Lucas shook his head, clutching my hand with an intensity that made my heart skip. “No, she’s here. In the house. I see her sometimes.”
A chill prickled at the back of my neck. I forced a smile, brushing it off as a child’s imagination running wild. “It’s just a dream, honey. Go to sleep.”

A woman forces a smile while sitting in her bed at night | Source: Midjourney
Lucas settled down, but I felt uneasy. I pushed the thought aside, telling myself he was just adjusting to a new family, a new normal. But as the days passed, small things around the house began to unsettle me.
For starters, I’d clean up Lucas’ toys, only to find them later exactly where I’d picked them up. Not just once or twice, but again and again.

A closeup of toy blocks scattered on the floor | Source: Pexels
And the kitchen cabinets — I’d rearrange them the way I liked, but the next morning, things were back in their old places, like someone was trying to undo my touch on the home. It was unnerving, but I kept telling myself it was just my mind playing tricks.
Then, one evening, I noticed something I couldn’t explain. I had moved Irene’s photograph from the living room to a more discreet shelf in the hallway. But when I came downstairs the next day, there it was, back in its original spot, perfectly dusted as though someone had just cleaned it.

A photo frame containing a woman’s picture | Source: Midjourney
I took a deep breath and decided to discuss it with Ben. “Are you moving things around the house?” I asked one evening, trying to sound casual as we were finishing dinner.
Ben looked up, grinning as though I’d told a silly joke. “No, Brenda, why would I? I think you’re just imagining things.”
He laughed, but there was something in his eyes — a hint of discomfort or maybe reluctance. I couldn’t place it, but I felt an invisible wall between us.

A man laughs to hide his discomfort | Source: Midjourney
A few nights later, Lucas and I were working on a puzzle on the living room floor. He was focused, placing the pieces with his little tongue poking out in concentration, when he suddenly looked up at me, eyes wide and sincere.
“Mom says you shouldn’t touch her things.”
My heart skipped a beat. “What do you mean, sweetie?” I asked, trying to keep my voice steady as I glanced toward the hallway.
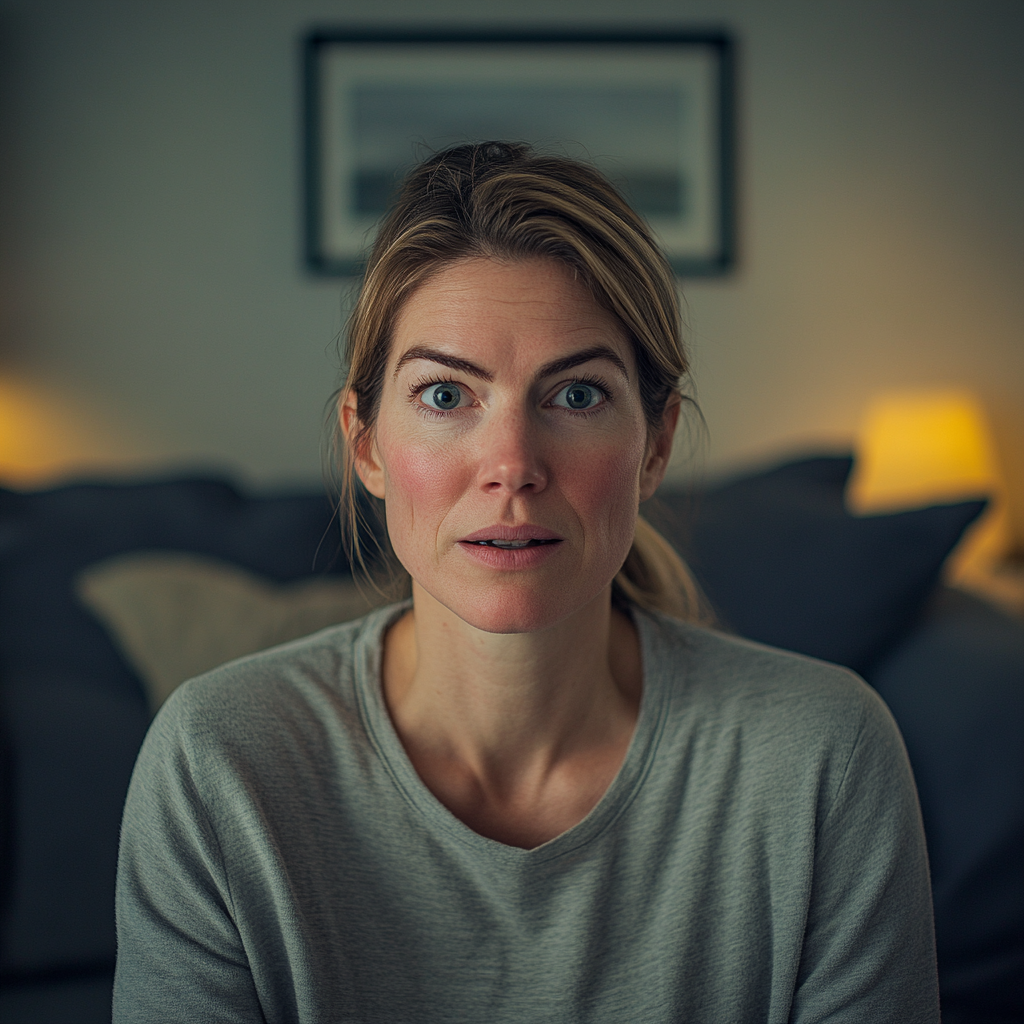

A stunned woman | Source: Midjourney
Lucas leaned in, lowering his voice. “Real Mom. She doesn’t like it when you move her things,” he whispered, glancing over his shoulder like he expected someone to be watching us.
I sat frozen, trying to process what he was saying.
The way he looked at me was so serious, like he was sharing a secret he wasn’t supposed to. I forced a smile, nodded, and gave his hand a gentle squeeze. “It’s okay, Lucas. You don’t have to worry. Let’s finish up our puzzle, alright?”

A closeup shot of a child making a puzzle | Source: Pexels
But that night, as Ben and I lay in bed, my mind raced. I tried to tell myself it was just a kid’s overactive imagination. But each time I closed my eyes, I’d hear Lucas’ words, see the way he’d glanced nervously toward the hallway.
When Ben was finally asleep, I got up quietly, heading to the attic. I knew Ben kept some of Irene’s old things in a box up there. Maybe if I could see them and find out more about her, it would help me understand why Lucas was acting this way.

A closeup shot of a metal box | Source: Pexels
I climbed the creaky stairs, my flashlight slicing through the dark, until I found the box tucked in a corner, dusty but well-kept.
The lid was heavier than I expected, as though it had absorbed years of memories. I pulled it off and found old photos, letters she’d written to Ben, and her wedding ring wrapped carefully in tissue. It was all so personal, and I felt a strange pang of guilt going through it.
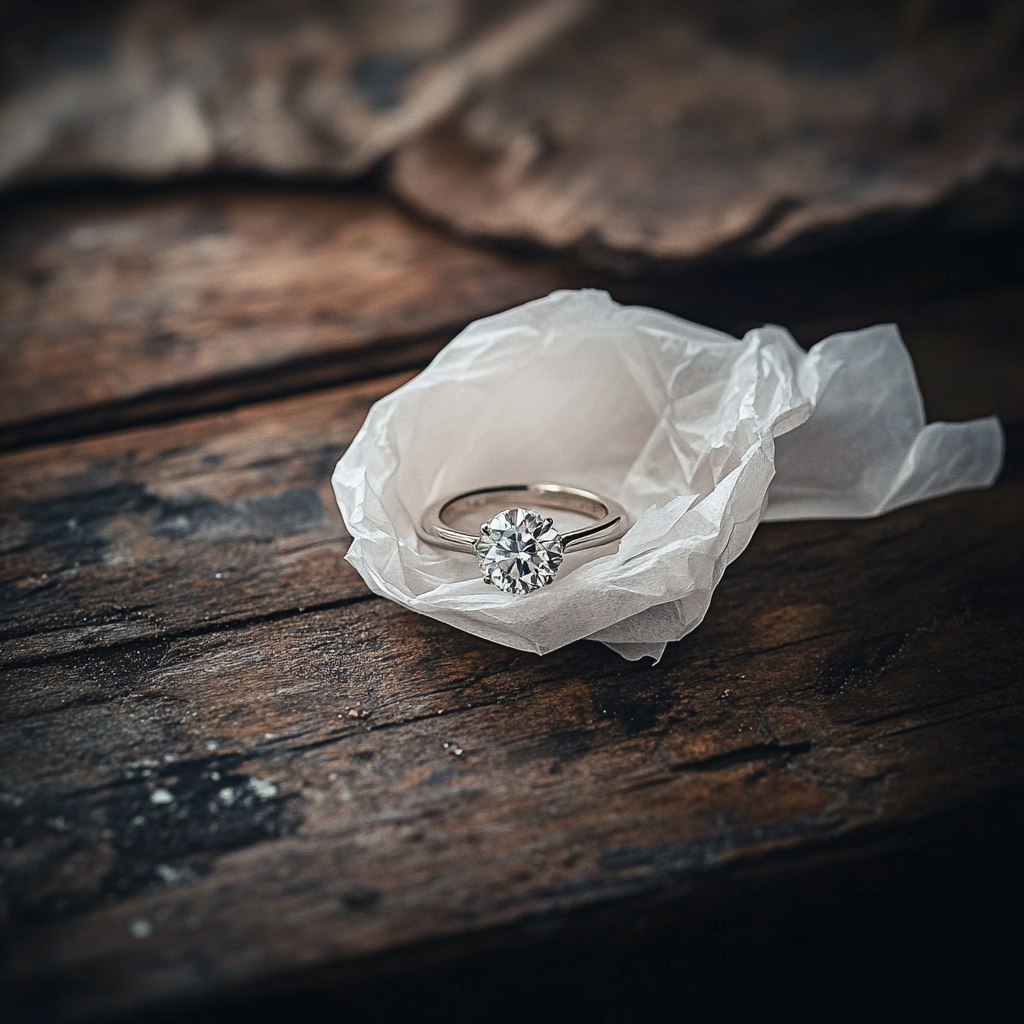

A wedding ring wrapped in a tissue lying on an old wooden table | Source: Midjourney
But there was something else. A few items looked freshly moved, almost as if they’d been handled recently. And that’s when I noticed it: a small door in the corner, half hidden behind a stack of boxes.
I froze, squinting at the door. I’d been in the attic a few times but had never noticed it. Slowly, I pushed the boxes aside and twisted the old, tarnished knob. It clicked, opening into a narrow room dimly lit by a small window.
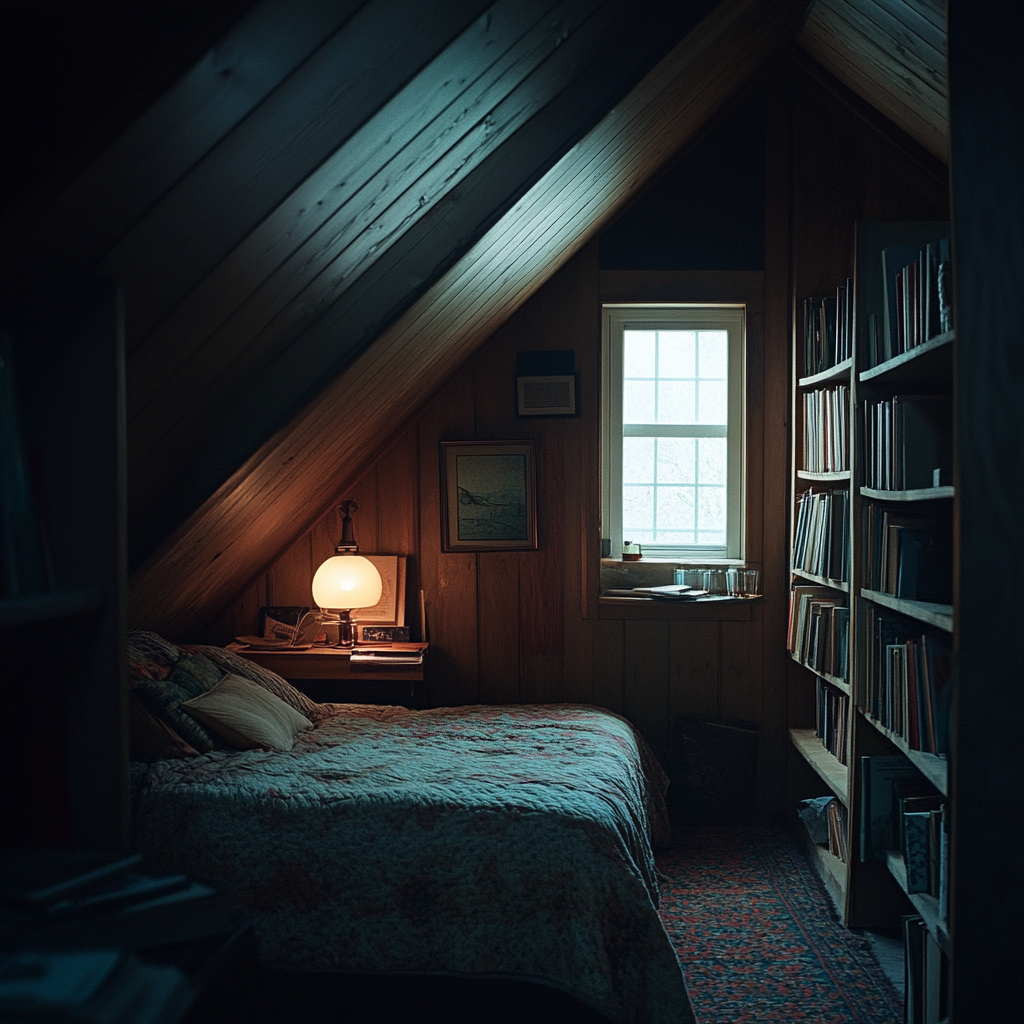

A narrow room dimly lit by a small window in an attic | Source: Midjourney
And there, sitting on a twin bed covered in blankets, was a woman I recognized immediately from the photos. She looked up, her eyes wide.
I stepped back, startled, and stammered, “You… you’re Emily, Ben’s sister, aren’t you?”
Emily’s expression shifted from surprise to something else — a quiet, eerie calm. “I’m sorry. You weren’t supposed to find out this way.”
I couldn’t believe what I was seeing. “Why didn’t Ben tell me? Why are you up here?”
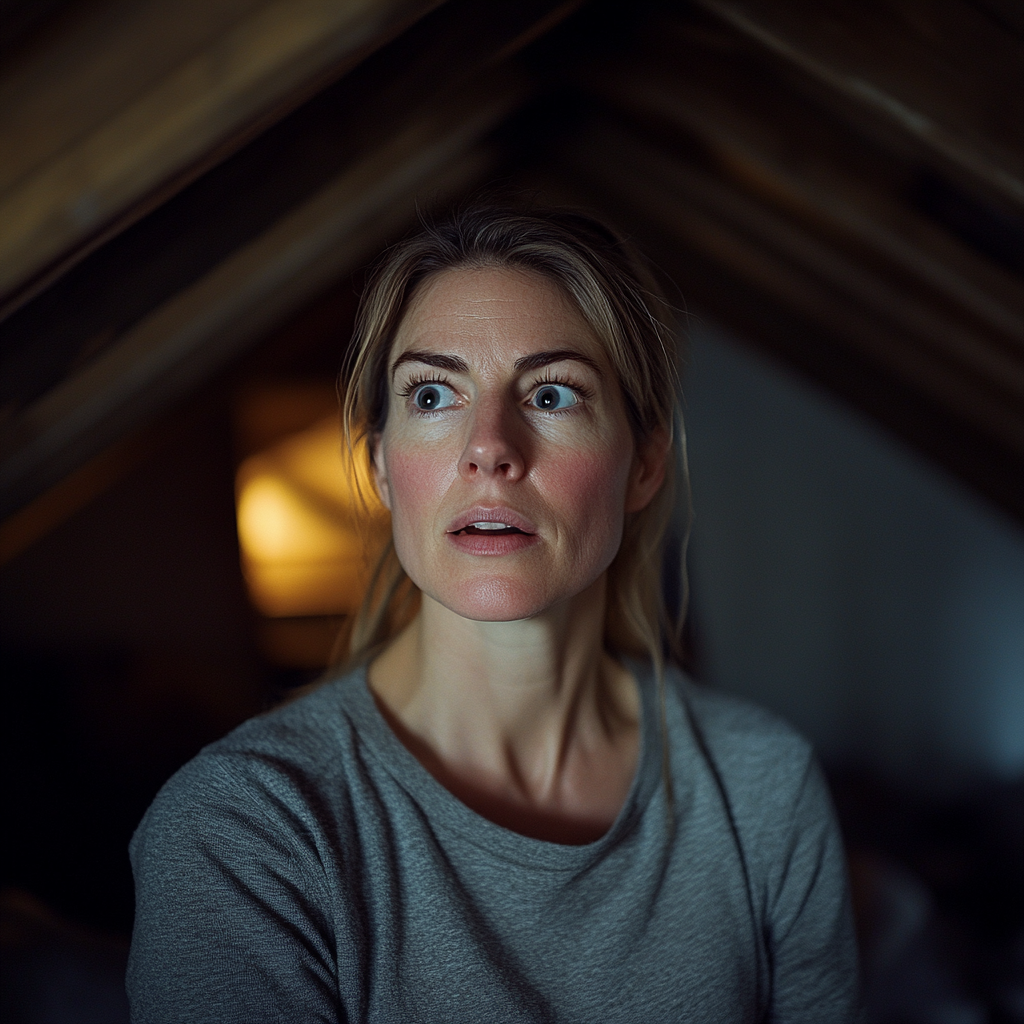

A woman is dumbfounded while standing in an attic | Source: Midjourney
She looked down, smoothing the edge of her blanket. “Ben didn’t want you to know. He thought you’d leave if you found out… if you saw me like this. I’ve… I’ve been here for three years now.”
“Three years?” I could barely process it. “You’ve been hiding up here all this time?”
Emily nodded slowly, her gaze distant. “I don’t… go outside much. I prefer it up here. But sometimes, I get restless. And Lucas… I talk to him sometimes. He’s such a sweet boy.”
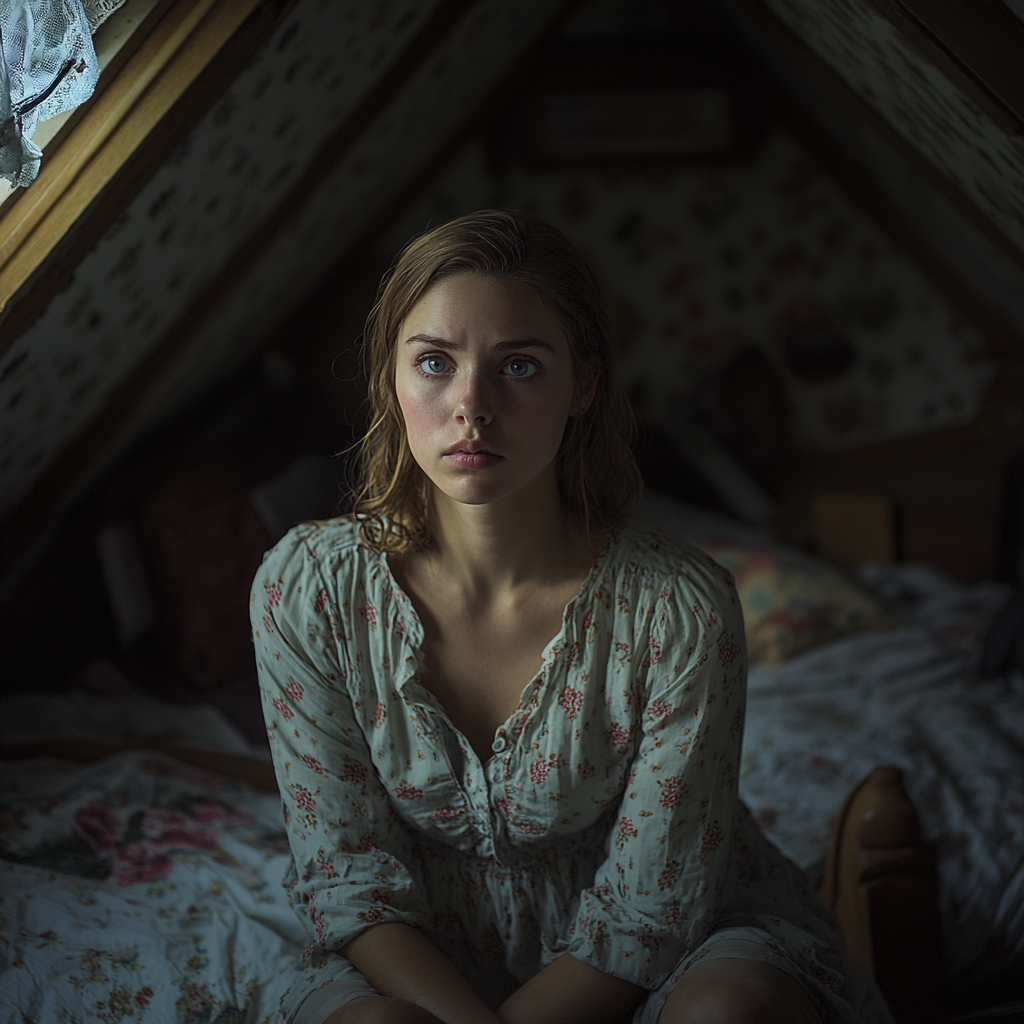

A woman sitting in an attic and looking at someone | Source: Midjourney
A chill ran through me. “Emily, what are you telling him? He thinks his mother’s still here. He told me that she doesn’t like it when I move things.”
Emily’s face softened, but there was a trace of something unsettling in her eyes. “I tell him stories sometimes. About his mother. He misses her. I think it comforts him to know she’s still… present.”
“But he thinks you’re her. Lucas thinks you’re his real mom,” I said, my voice breaking.
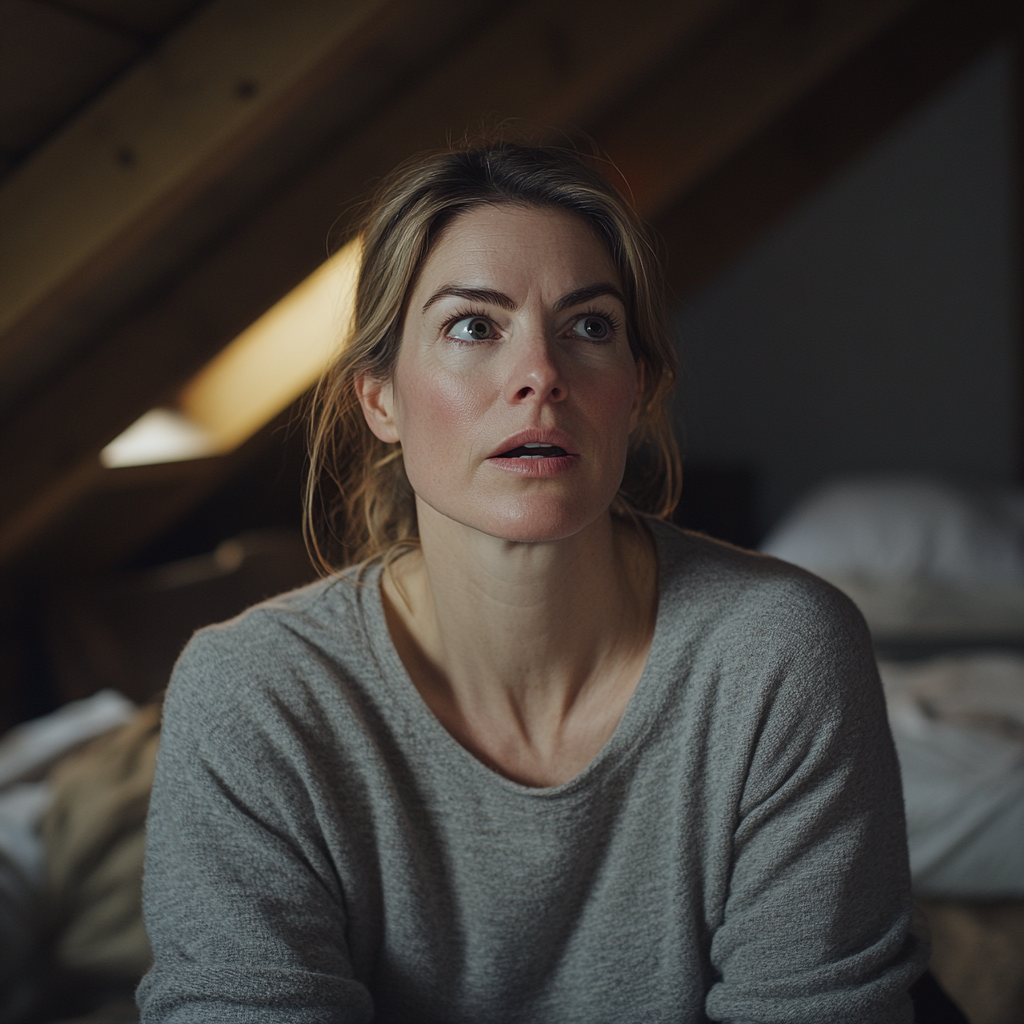

A shocked woman in an attic | Source: Midjourney
She looked away. “Maybe it’s better that way. Maybe it helps him to feel she’s still here.”
I felt my head spinning as I backed out of the room, closing the door behind me. This was beyond anything I could have imagined. I went straight downstairs, finding Ben in the living room, his face immediately full of concern when he saw me.
“Ben,” I whispered, barely holding it together. “Why didn’t you tell me about Emily?”
He went pale, his eyes darting away. “Brenda, I—”

A surprised man looking at someone | Source: Midjourney
“Do you realize what she’s been doing? Lucas thinks… he thinks she’s his real mom!”
Ben’s face fell, and he sank onto the couch, his head in his hands. “I didn’t know it had gotten that bad. I thought… I thought keeping her here, out of sight, would be best. I couldn’t leave her alone. She’s my sister. And after Irene passed, Emily wasn’t the same. She refused to get any help.”
I sat beside him, gripping his hand. “But she’s confusing Lucas, Ben. He’s just a child. He doesn’t understand.”

A woman looking kind and concerned | Source: Midjourney
Ben sighed, nodding slowly. “You’re right. This isn’t fair to Lucas—or to you. We can’t keep pretending like everything’s fine.”
After a few moments, I whispered, “I think we should set up a camera, just to see if she’s really been leaving her room. To know for sure.”
Ben hesitated, but eventually, he agreed. We set up a small, hidden camera outside Emily’s door that night.
The next evening, after Lucas had gone to bed, we sat in our room, watching the footage. For hours, nothing happened. Then, just past midnight, we saw her door creak open.

A grayscale shot of an open attic door | Source: Midjourney
Emily stepped into the hallway, her hair loose around her face, and stood there, looking at Lucas’ bedroom door.
Then Lucas appeared, rubbing his eyes, and walked toward her. Even on the grainy screen, I could see his little hand reaching for her. She knelt down, whispering something to him, her hand on his shoulder. I couldn’t hear the words, but I saw Lucas nod and say something back, looking up at her with that same, earnest expression.

A young boy standing in his room | Source: Midjourney
I felt a wave of anger and sadness I couldn’t quite control. “She’s been… she’s been feeding his imagination, Ben. This isn’t healthy.”
Ben watched the screen, his face drawn and tired. “I know. This has gone too far. We can’t let her do this to him anymore.”
The next morning, Ben sat down with Lucas, explaining everything in simple terms. He told him that his Aunt Emily was sick, that sometimes her illness made her act in ways that confused people, and that his real mom wasn’t coming back.

A father talking to his young son | Source: Midjourney
Lucas was quiet, looking down at his little hands, and I could tell he was struggling to understand. “But she told me she’s my mom. You can’t send her away, Dad,” he murmured, his eyes filling with tears.
Ben hugged him tightly, his voice thick with emotion. “I know, buddy. But that was her way of trying to help you feel close to your mom. She loves you, just like we do. And we’re going to help her get better.”

A woman standing in an attic | Source: Midjourney
Later that day, Ben arranged for Emily to see a doctor. The process was painful; she protested, even cried, but Ben stayed firm, explaining that she needed help. Once she was admitted to the hospital, the house felt quieter, almost lighter.
Lucas struggled at first. He’d ask about Emily, sometimes wondering if she was coming back. But gradually, he began to understand that what he’d believed wasn’t real, and he started to make peace with the truth.
Through it all, Ben and I grew closer, supporting each other as we helped Lucas cope.

A happy couple | Source: Midjourney
It wasn’t the journey I expected when I married him, but somehow, we’d come out stronger on the other side, bound together not just by love, but by everything we’d faced as a family.
If you loved this story, here’s another one for you: When Ruth entered her in-laws’ house, she sensed something was wrong. The unsettling silence and her father-in-law’s strange text were just the beginning. But when she followed a mysterious noise to the attic and unlocked the door, nothing could have prepared her for what she found.

A shocked woman | Source: Midjourney
This work is inspired by real events and people, but it has been fictionalized for creative purposes. Names, characters, and details have been changed to protect privacy and enhance the narrative. Any resemblance to actual persons, living or dead, or actual events is purely coincidental and not intended by the author.
The author and publisher make no claims to the accuracy of events or the portrayal of characters and are not liable for any misinterpretation. This story is provided “as is,” and any opinions expressed are those of the characters and do not reflect the views of the author or publisher.



Leave a Reply